The Mental Health Effects of Chronic Pain: A Deep Explanation
Many people are struggling with ongoing chronic pain in daily life. It’s not just a physical condition, but it becomes a mental burden to deal with. The persistent pain not only affects your daily life but also your mental health and emotional well-being. The mental health effects of chronic pain are complex and overlooked as people become used to it. But it’s not the solution.
It is necessary to understand its consequences and treat it completely. In this article, we will explore how chronic pain impacts your mental health and how to cope with it.
What is Chronic Pain?
First, we understand chronic pain and how it is different from normal pain. The pain that does not heal for a long time(up to 3 months or beyond expectation) and continues to come and go is chronic pain. For example:
The pain arises from:
- Arthritis
- Fibromyalgia
- Neuropathy
- Migraines
- Back pain
- Autoimmune diseases
Whereas the normal pain or acute pain is a short-term, sudden, sharp pain that occurs due to an injury or disease. It’s gone within days or weeks.
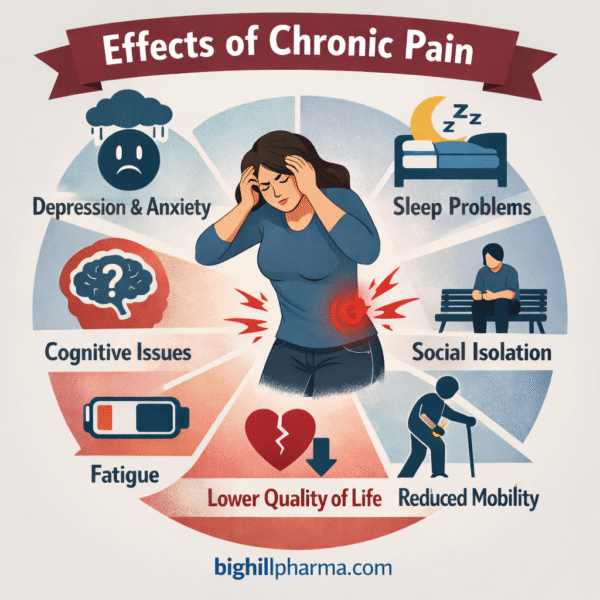
Effects of Chronic Pain on Mental Health
Chronic or persistent pain can exhaust your mental health. As the body and brain are interconnected, long-term pain causes changes in brain function and chemistry. Thus, the risk of developing mental health disorders like depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), substance use disorders, etc., increases.
Major Mental Health Effects of Chronic Pain in Detail
The following are the psychological effects of living with chronic pain:
-
Depression
One of the most common psychological effects due to chronic pain is depression. More than 50% of people with chronic pain experience major depressive disorder.
Why does it happen?
- The brain chemicals like serotonin and dopamine stimulate the mood changes, which get disrupted by the persistent pain.
- Loss of mobility, independence, or work can activate emotions of distress.
- The constant discomfort results in an emotional burden that can drain energy and motivation.
Symptoms include:
- Low mood
- Loss of interest or pleasure
- Changes in appetite or sleep
- Fatigue
- Suicidal thoughts
2. Anxiety and Fear
Dealing with prolonged pain often brings fear, like fear of the next pain outburst, of worsening health, etc.
Anxiety disorders related to chronic pain are:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
- Panic disorder
- Health anxiety or hypochondriasis
Effects:
- Constant nervousness
- Muscle tension
- Rapid heartbeat
- Avoid participating in activities due to fear of triggering pain
3. Cognitive Impairment (“Brain Fog”)
Another key mental health effect of chronic pain is cognitive impairment that interferes with concentration, memory, and mental clarity.
Possible causes:
- Mental fatigue from constant discomfort
- Disrupted sleep patterns
- Changes in brain structure due to long-term pain
Symptoms:
- Memory loss
- Difficulty concentrating
- Slowed thinking or speech
- Trouble with decision-making
4. Sleep Disorders
If you have severe pain for a long time, your sleep gets disturbed, and a lack of sleep worsens pain sensitivity.
Sleep-related issues include:
- Difficulty falling asleep
- Frequent night awakenings
- Poor sleep quality
- Insomnia
Psychological impact:
- Increases irritability
- Emotional instability
- Risk of depression
5. Social Withdrawal and Isolation
If you have pain in your body, you don’t want to participate in social activities, work, or family events.
Psychological Effects:
- Results in isolation
- Feeling lonely and a sense of disconnection
- The risk of depression and anxiety increases
6. Low Self-Esteem and Loss of Identity
Chronic pain can deeply affect a person’s sense of self. Disruptions to daily activities—like work, parenting, or exercise—can lead to an identity crisis.
Common feelings include:
- Feeling guilty
- Feeling like a burden to others.
If these negative thoughts continue, they can cause emotional damage to the person.
7. Substance Use and Coping Challenges
Due to this chronic pain and depression cycle, some individuals start taking alcohol, prescription painkillers, or recreational drugs to numb both physical and emotional pain.
Dangers:
- Risk of dependency or addiction
- Increased depression and anxiety
- Deteriorating health and pain over a prolonged span
Proper mental health support can help reduce reliance on substances as a coping mechanism.
How to Cope With the Mental Health Effects of Chronic Pain?
The following strategies can help a person to come out of depression and other mental health conditions:
1. Psychotherapy
It includes:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Works on changing negative thinking to positive.
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT): Makes you strong enough to accept pain while focusing on your life goals.
2. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Meditation, breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can help the depressive person reduce stress and improve pain tolerance.
3. Support Groups and Peer Networks
Joining groups that are experiencing similar challenges can offer emotional relief and coping strategies.
4. Medication
Antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and mood stabilizers are also prescribed alongside pain medications when needed to deal better with the effects of Chronic pain.
5. Physical Activity and Movement
Walking, stretching, or yoga can help release endorphins, improve mobility, and enhance mood.
6. Lifestyle Changes
Taking a healthy diet, quality sleep, routine, and reducing alcohol/caffeine intake can support both physical and mental well-being.
Summarizing the Topic “The Mental Health Effects of Chronic Pain”
The mental health effects of chronic pain are profound and far-reaching, affecting mood, cognition, relationships, and overall quality of life. Recognizing the psychological impact of pain is essential for effective management. A holistic treatment procedure may address both the body and the mind. So individuals can reclaim control, hope, and resilience in the face of chronic suffering.
FAQs
Q1: Does chronic pain cause mental illness?
Prolonged severe pain conditions can lead to mental illnesses like depression, anxiety, and cognitive impairment due to changes in brain function and chemicals.
Q2: How does chronic pain affect mood?
The effects of chronic pain on mood are irritability, sadness, frustration, and emotional exhaustion.
Q3:Name the Psychotherapy that helps in dealing with the Mental Health Effects of Chronic Pain.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)